Out of all the injuries you may encounter throughout your life, burn injuries are among those that pose some of the greatest dangers. Depending on various factors, inclusive of the source of the burn and its location, burn injuries can involve both immediate and prolonged medical attention. Fatal burns require incredibly long recovery time. So what percentage of body burned is fatal. This article explores facts about fatal burn injuries.
How do you know a burn is severe?
What percentage of burns is fatal?
Human skin is the largest organ of the body. It provides a protective barrier to the outside environment, preventing harmful bacteria and other materials from entering the body. Typically it is made up of:
- Epidermis layer- it is the outer surface of the skin, and it shields the body from the environment.
- Dermis layer- the second layer of the skin and has sensory nerves, oil glands, and sweat glands and hair follicles.
- Subcutaneous layer- it is the third innermost layer of your skin and contains soft and fatty tissues that lie just beneath the dermis.
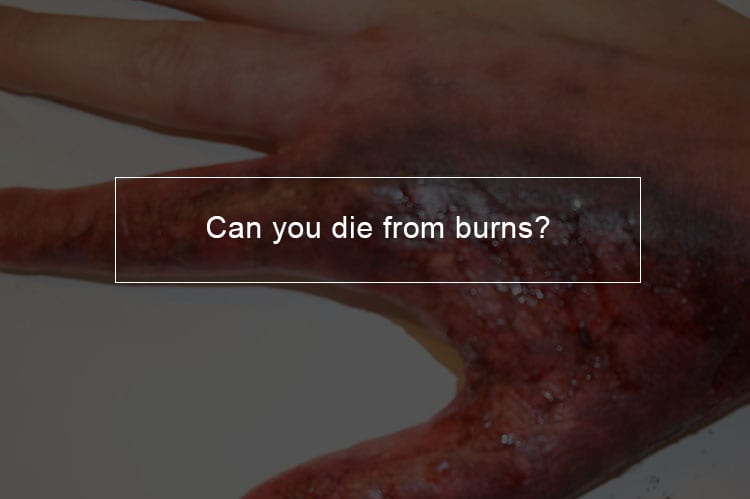
The severity of the burns
When heat or chemicals come in contact with your skin, the damage is done to its chemical and cellular makeup. Dependent on how hot your skin gets, how long it is exposed to the source and the physical location of the burn, doctors can diagnose the severity of a burn.
4th degree burns
These burns extend beyond all three layers of skin and deep into the muscle tissue or bone. Fourth-degree burn injuries frequently result to complete loss of function in the burned region. They require tissue removal and can even result in death.
6th degree burns
6th degree burns are the most severe burns. Mainly, 6th burns lead in charring and loss of function of the affected region.
Charring is the process where exposure to high heat burns the hydrogen and oxygen from the skin. The process leaves a black substance comprised of almost entirely carbon. The presence of char in a burn is an indicator that the burn will need grafting and leave scars. Charring can occur in third-degree burns, but it is more common with deeper burns that have had more prolonged exposure to a heat source.
These burns also destroy the skin's protective capabilities and begin to damage the underlying muscle. Unfortunately, the body does not regrow muscle or bone in the same way that it regrows skin. Damage to the muscle often requires excision and leads to long-term loss of function of the affected area. Loss of function generally leads to amputation.
Burn percentage calculation
Doctors will do a visual examination to look for severely burned areas and use the rule of nines to add up what percentage of a person's body is burned. While doctors will perform more thorough assessments for burn estimation, they can use the rule of nines to assess a person. The rule of nines assigns a percentage that is either nine or a multiple of nine to determine how much body surface area is damaged. For adults the rule of nines is:
- Arm inclusive of the hand; nine percent each
- Anterior trunk (front of the body); eighteen percent
- Genitalia; one percent
- Head and neck; nine percent
- Legs inclusive of feet; eighteen percent each
- Posterior trunk (back of the body); eighteen percent
If a person is injured because of a burn, the doctor may assess them quickly. For instance, if you were burned on every hand and arm as well as the from trunk portion of the body, using the rule of nines, using the rule of nines, they would estimate the burned area as 36 percent of a human's body. If burns exceed thirty percent of a person's body can be possibly fatal.
How can you survive a 6th degree burn?
6th degree burn survival tips
These steps may help reduce the severity of a burn once it occurs:
- Giving first aid immediately
- Getting prompt medical attention
- In the case of hospitalization, being treated by a dedicated burn unit with staff specially trained in burn care is essential.
Common causes of 6th degree burns
Nearly any cause of a burn can create a sixth-degree burn, so long as there is prolonged exposure. The extended time of contact allows the burn source not just to destroy the epidermis, but also to burn down to the bone. Persons are likely to suffer from a sixth-degree burn if they are in a fire, radiation exposure, explosion, or cooking accident or even contact with high levels of voltage through an electrical appliance or connection. Even fighters, who go through training to enter burning buildings, are at risk of these more severe burns to work hazards.
Preventive burns care
- These practices may reduce your risk for burns
- Installing smoke sensors
- Teaching children about fire and burn in schools
- Avoid smoking and heavy alcohol use
- Planning emergency exit routes in the home, school, and workplace
- Practicing fire drill
How do burns cause death?
The immediate cause of death in a burn
Burning to death might be the worst way possible to die. Human flesh does not catch fire easily so burning to death can be slow and painful. The0re are several ways people can die from fire, but until one loses consciousness, then one is going to be in agony. Below are the immediate causes of deaths ins burn:
Carbon monoxide burn death
When individuals are executed by being burned, they might pass on from carbon monoxide harming the flares cause serious harm to the body. This only happens in expansive fires, where numerous individuals are executed at once.
Fire peels burn death
A fire will to begin with burn and peel away the epidermis - the thin external layer of skin. After five minutes under fire, the thicker layer of skin - the dermis - shrivels and parts open, and fat starts to spill out, resulting in the death of an individual.
Thermal decomposition death
Thermal decomposition during the fire as the immediate cause of death during burning Another cause of death by fire is the thermal decay of essential organs or body parts. Organs that you require to live to get devastated by the heat or the fire itself.
Shock as an immediate cause of death in a fire
Dying of stun, like carbon monoxide, would be a tolerant way to for a person in case they were being burned alive. The starting pain of the fire may well be so severe that your body may go into initial shock. The blood pressure abruptly drops so low that imperative organs can no longer work.
Death from loss of blood
If in case of fire an individual does not die of carbon monoxide poisoning or shock, the other likeliest cause of death will be loss of blood or liquids, also known as hypovolemia. Extreme burns to the skin trigger an incendiary reaction, which causes capillaries to spill. In case the capillaries spill too much blood, the individual might die.
Suffocation in a fire can cause death
Another possible cause of death in a fire is suffocation. The throat could become so swollen and blistered from breathing in hot air and fumes that you would be unable to take in any more oxygen.
Death from heart stroke
If your temperature rises over 105 degrees Fahrenheit, the enzymes inside your body won't be able to operate properly. This leads to major organ failure, which comes about in death.
Dangers of Severe Burns
Severe or extensive burn injuries can pose a few serious issues. A few of the primary common threats are:
Infection and sepsis burn: Burn wounds leave your skin open and vulnerable to infection. Without healthy skin, you've got no defense against bacterial infections. Burn injuries to increase your chance of sepsis, which may be a life- undermining contamination that quickly travels through the circulatory system. Sepsis can cause stun and organ failure.
Low Blood Volume: Burn injuries harm your blood vessels, causing liquids to escape the body. This could result in low blood volume, known as hypovolemia. A severe loss of liquid and blood can prevent the heart from pumping sufficient blood through your body.
Breathing Difficulties: One of the foremost common dangers that go with burn wounds is the inhalation of smoke or hot air. This could burn your airways, making it difficult to breathe. Smoke can permanently harm your lungs and lead to respiratory failure.
Problems with Bones and Joints: More profound burns can severely restrain any movement for bones or joints. Burn wounds form scar tissue once mended and can cause contractures. When the skin is burned, encompassing skin begins to pull together, coming about in a post-burn contracture that prevents movement.
Whereas only a portion of burn wounds result in third or fourth-degree burns, any burn harm can posture serious threats and lead to complications. If you received a burn injury resulting from another party's carelessness, you have the right to look for compensation for your misfortunes.
How many people die from burns?
Burn victims
According to the American Burn Affiliation (ABA), there are roughly 3,400 U.S. burn damage death cases each year. Burn injury death is frequently caused by burn complications, such as stun, organ disappointment, respiratory issues, or contamination. To avoid burn damage passing, severe burn patients ought to get crisis therapeutic attention to guarantee a steady condition before burn wound treatment starts.
The majority of burn injury death cases result from arising complications, not the burn damage itself. The shock could be a common cause of burn injury death. Burn damage passing from shock regularly happens inside a week of the occurrence.
Sepsis burn
Burn sepsis is one of the usual fatal burn injury complications. In spite of medical advancements, burn sepsis accounts for 50-to-60 percent of burn injury deaths. Burn sepsis occurs after a burn injury patient develops an infection. The condition may also occur as a result of other types of infection that occur during the treatment process, such as pneumonia from breathing tubes or urinary tract infection from bladder catheters.
Burn destruction to the skin most frequently caused by flame or fire or steam and hot liquids. Burns can result from chemicals, hot objects, or even electricity. The range from the mild to severe, and whereas severe burns can be life-threatening, any burn results to a break in the skin can lead to an infection which can cause sepsis.
Sometimes mistakenly known as blood poisoning, sepsis is the body’s frequent deadly response. Sometimes mistakenly known as blood poisoning, sepsis is the body’s frequently fatal response to infection. Sepsis burn kills and disables millions and requires early suspicion and treatment for survival.
Sepsis and septic shock can result from an infection anywhere in the body, such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and influenza. If sepsis is not treated, the patient may go into septic shock. A dramatic drop in blood pressure characterizes septic shock. This can result in organ failure and death.
Septic shock patients typically also experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, abnormal heart function, abdominal pain, and confusion or disorientation.Burn sepsis survival rates are highest in patients with early diagnosis and aggressive treatment. Severe burn sepsis requires careful monitoring in the intensive care unit of a medical facility. Many patients require stabilization of heart function and breathing. Burn sepsis patients may receive supportive therapies such as oxygen and plenty of intravenous (IV) fluids.




