Eczema can be both fungal or bacterial infection. A bacterium known as Staphylococcus aureus, which thrives on weepy and broken skin, is very common in eczema. Infection can produce a pattern identical to many types of eczema.
Different stages and kinds of eczema affect about 31.6 percent of people in the United States. The term"eczema" is also used particularly to refer to atopic dermatitis, the most prevalent type of eczema. "Atopic" applies to a collection of diseases pertaining to the immune system, like atopic dermatitis, asthma, and hay fever. Dermatitis is an inflammatory malady of the skin. Some outgrow the disease, while others continue to have it throughout adulthood.
What is the difference between fungal infection and bacteria eczema?
A fungal infection is caused by the fungus candida even though a few other fungal may also result in an infection. While eczema has several causes, but the usual one is atopic dermatitis as a result of lifelong acquired genetic predisposition to allergens. There are numerous kinds of fungal infections such as candidiasis, diaper rash, body rash, and many others- all fungal infections have diverse signs and symptoms depend on the part of the body they occur. For eczema, whether it occurs as a result of atopic dermatitis or allergic contact dermatitis, the appearance is the same.
Unfortunately, the signs and symptoms of fungal infections may vary dependent on the place of the infection; some could occur as a red rash, whereas others might be itchy, hot, and painful. Some fungal infection generates softened, red skin in body skinfolds, while others occur as discolored nails on fingers and toes. Eczema signs and symptoms typically progress from the first intense itches and could burn. Cracks in the skin could develop, and patients may get puffy, itchy red eyelids.
Eczema causes include low humidity, exposing skin to solvents, food allergies, over washing of the skin with harsh soaps and detergents and lotions and also occasional wetting and drying of the skin, among other factors. Contrary, fungal infections are caused by skin regions which are frequently moist and subjected to friction, tight-fitting clothes and shoes, and alteration of the immune system.
Fungal infection is typically treated using antifungals such as polyene antifungal medications and azole medications while eczema uses anti-inflammatory treatments and steroid lotions together with topical moisturizers and emollients to inhibit water loss from the skin. Fungal infection typically has a good prognosis and can be treated in many individuals, while eczema may reduce in adulthood, but some of the individuals who have this illness frequently have lifelong issues and eye irritations.
What is eczema?
An in-depth examination of the causes of eczema
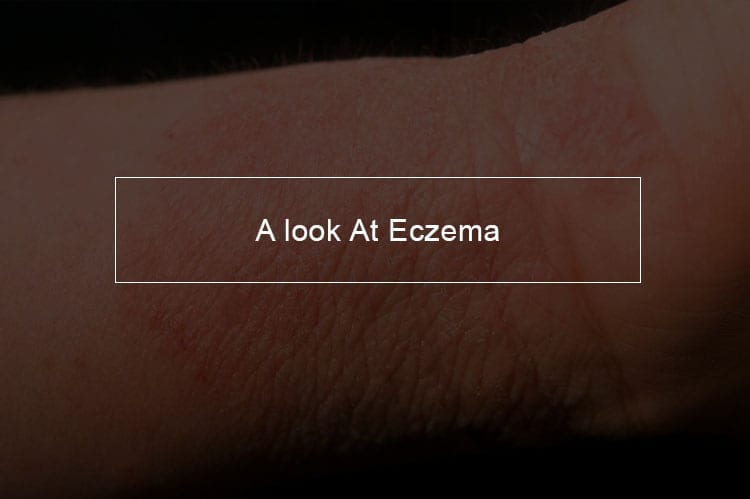
Rather than a specific health problem, eczema is a reaction pattern that the skin makes in some diseases. It starts as red, raised tiny blisters with a clear fluid atop red, elevated plaques of skin. When the blisters pop, the affected skin weeps and oozes. In older or chronic eczema, the blisters are less noticeable, and the skin is thickened, raised, and scaly. Eczema almost always is very itchy.In general, eczema can afflict the skin by causing:
- darkened patches
- rough, scaly, or leathery patches
- inflammation
- crusting and oozing of blistered skin
Eczema is not contagious; thus a person cannot catch it or pass it onto another person.
Facts about Eczema
- Eczema is not a singular health condition but a recognizable reaction pattern seen in many skin diseases.
- Atopic dermatitis, a common cause of eczema, is more common in those with asthma or hay fever.
- Eczema signs and symptoms include getting tiny blisters (known as vesicles) that can weep and ooze fluid, eventually producing crusted, thickened plaques of cutaneous tissue. It is almost always very itchy.
- Symptoms of the condition differ depending on the age of the person with eczema, but they usually include getting scaly, itchy patches of skin.
- It is crucial to distinguish the various causes of eczema because their effective treatments often differ.
- Eczema flare-ups can also be caused by environmental factors such as smoke, or pollen. Eczema, however, is not a curable disease.
- Certain foods like nuts and dairy can trigger symptoms.
- If eczema is caused by the exposure of skin to a specific substance, it can be advantageous to avoid it.
- Treatment focuses on treating the damaged skin and alleviating the symptoms. There isn't a full cure for eczema yet, but its symptoms can be managed.
- Eczema is not a contagious condition.
- Keeping the skin healthy and moisturized can stop certain types of eczema.
Causes of eczema
Pollen is among the many potential triggers of eczema flare-ups.The precise cause of this skin disease remains unknown, but it is believed to happen due to a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Eczema is not contagious.Children are more likely to get eczema if one parent has had the skin condition or other atopic conditions.If both parents have an atopic skin condition, the risk is even greater.Environmental factors also trigger symptoms of eczema, like:
Irritants: Soaps, detergents, shampoos, disinfectants, juices from fresh fruits, meats, or vegetables.Allergens: These include dust mites, pets, pollens, mold, and dandruff can cause eczema.
Microbes: Bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, viruses, and certain fungi can cause eczema.Hot and cold temperatures: Very warm or cold weather, high and low levels of humidity, and perspiration from working out can bring out eczema.
Foods: Dairy and its products, eggs, nuts and some seeds, soy products, and wheat can trigger eczema flare-ups.
Stress: This isn't a direct cause of eczema but makes the symptoms worse.
Hormones: Women can get increased eczema flare-ups at times when their hormone levels are varying, for instance during pregnancy and at certain times in the menstrual cycle.
What are eczema symptoms and signs?
Almost all people with eczema lament of itching. Since the appearance of most kinds of eczema is similar, the distribution of the eruption can help distinguish one kind from another. For instance, stasis dermatitis occurs mostly on the lower leg while atopic dermatitis occurs in the front of the elbow and behind the knee.
Typically the first sign of eczema is intense itching. The rash forms later and is red and has swellings on different sizes. The rash may feel itchy with a burning sensation, particularly in thin skin like the eyelids. In case it is scratched the itch can ooze and become crusty.
In adults, persistent rubbing generates thickened plaques of skin.The rash may develop in more round areas, a condition which is known as nummular eczema and is easily confused with fungal infection. Some patients form red bumps or clear fluid packed bumps which, when scratched add wetness to the overall appearance.
Painful cracks in the skin can also form over time. Even though the rash can occur anywhere on the body, in both children and adults, it frequently forms on the neck, arms, and flexures of legs.
Are there different kinds of eczema?
There are about 11 distinct kinds of skin conditions that cause eczema. To form a rational treatment plan, it is important to identify them. This is often not as easy as it sounds.
Atopic dermatitis
This health condition has a genetic cause and produces a common kind of eczema. Atopic dermatitis tends to start early in life in persons with an inclination to inhalant allergies, but it presumably does not have an allergic cause. Characteristically, rashes appear on the cheeks, neck, elbow and knees, and ankles.
Allergic contact dermatitis
After repeated exposure to the same thing, an allergen, the body's immune identification system becomes activated at the place of the next exposure and causes dermatitis. An illustration of this would be poison ivy allergy.
Irritant dermatitis
It is a form of contact dermatitis, in which the skin is injured by friction, environmental factors like cold, over-exposure to water, or chemicals such as acids, alkalis, detergents, and solvents.
Stasis dermatitis
It usually occurs on the swollen lower legs of persons who have poor circulation in the veins of the legs.
Fungal infections
These infections can produce a pattern identical to many types of eczema. These outbreaks can be treated with antifungal medication.
Scabies
It's prompted by an infestation by the human itch mite and can produce a rash very similar to other kinds of eczema.
Pompholyx (dyshidrotic eczema)
This is a widespread but poorly understood health condition which classically affects the hands and occasionally the feet by producing an itchy rash composed of tiny blisters (vesicles) on the sides of the fingers or toes and palms or soles.
Lichen simplex chronicus
It produces thickened plaques of cutaneous tissue found on the shins and neck.
Nummular eczema
This is a general term for coin-shaped plaques of scaling skin most often appearing on the lower legs of older individuals.
Xerotic (dry skin) eczema
It is a form of eczema characterized by variations that occur when skin gets abnormally dry, red, itchy, and cracked. It tends to happen more during the winter and in dry weather conditions. The lower legs tend to be affected, although it can appear in the underarm area as well.Xerotic eczema is prevalent in seniors, though it is not uncommon in younger people in their 20s. It can appear red, bumpy, pimple-like irritations. Shaving can cause inflammation.
Seborrheic dermatitis
It causes a rash on the scalp, face, ears, and sometimes the mid-chest in adults. In babies, it can cause a weepy, oozy rash behind the ears and can be very extensive, involving the entire body.
Eczema Treatment options

There is currently no cure for eczema. Treatment aims to treat the affected area and prevent flare-ups of symptoms. Doctors suggest a treatment plan based on the person's age, symptoms, and the current state of health. For some, eczema goes away on its own over time. For others, it is a lifelong condition.
Home care
There are many things that persons with eczema can do to improve skin health and alleviate symptoms, like: taking lukewarm baths, not hot onesapplying your preferred moisturizer within 3 minutes of showering to "lock in" moisturemoisturizing dailywearing clothes made of cotton or soft fabrics, and keep away from rough, scratchy materials and tight-fitting clothingusing a mild soap or a non-soap cleanser whenair drying or gently patting the skin dry with a towel, rather than rubbing it dry after bathingwhenever possible, avoiding rapid differences in temperature and activities that cause you to sweatlearning and avoiding individual eczema triggersusing a humidifier during dry or cold weatherkeeping your fingernails short to stop you from scratching and breaking the skin and causing infections.
Medications and treatments
There are several kinds of medications that medical practitioners can prescribe to treat the symptoms of eczema, like:
Topical corticosteroid creams and ointments - These are a kind of anti-inflammatory medication and work to relieve the main symptoms of eczema, like inflammation and itchiness. They are put on directly to the skin. If you would like to purchase topical corticosteroid creams and ointments, you can get them online or over the counter.
Systemic corticosteroids - If topical treatments are not effective in treating eczema, systemic corticosteroids can be used. These are either injected or taken orally, and they are only used for short whiles. -
Antibiotics
These are prescribed if eczema occurs together with a bacterial skin infection.
Antiviral and antifungal medications
These are used to treat fungal and viral infections that happen.
Antihistamines
These decrease the risk of nighttime scratching as they can cause drowsiness.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors
This is a kind of drug that suppresses the immune system. It lessens inflammation and aids prevent flare-ups.
Phototherapy
This requires exposure to UVA or UVB waves, alone or combined. The skin should be monitored carefully. This technique is normally used to handle moderate dermatitis.Even though the condition itself is not yet curable, there should be a particular treatment plan to suit each person with different symptoms. Even after an area of skin has healed, it is important to keep looking after it, as it may easily become irritated again.




